Cytidine diphosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Cytidine 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.507 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C9H15N3O11P2 |
| Molar mass | 403.176422 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
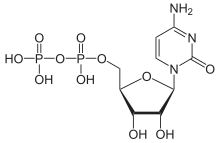
Cytidine diphosphate, abbreviated CDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside cytidine. CDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase cytosine.
In Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, CDP-activated glycerol and ribitol are necessary to build wall teichoic acid.[1]
In Rhodothermus marinus, CDP-activated inositol is necessary to form the phospholipid dialkylether glycerophosphoinositide, which contains inositol phosphate and ether-linked alkyl chains.[2]
CDP is commonly formed in the reaction Dolichol + Cytidine Triphosphate (CTP) ⟶ Dolichol-phosphate + CDP, which is prevalent in many biochemical pathways.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Pereira, Mark P.; Brown, Eric D. (2010-01-01), Holst, Otto; Brennan, Patrick J.; Itzstein, Mark von; Moran, Anthony P. (eds.), "Chapter 19 - Biosynthesis of cell wall teichoic acid polymers", Microbial Glycobiology, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 337–350, ISBN 978-0-12-374546-0, retrieved 2021-12-08
- ^ Jorge, Carla D.; Borges, Nuno; Santos, Helena (July 2015). "A novel pathway for the synthesis of inositol phospholipids uses cytidine diphosphate ( CDP )-inositol as donor of the polar head group". Environmental Microbiology. 17 (7): 2492–2504. Bibcode:2015EnvMi..17.2492J. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12734. ISSN 1462-2912.
- ^ PubChem. "Cytidine-5'-diphosphate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-04-27.
- v
- t
- e
- Purine
- Pyrimidine
- Unnatural base pair (UBP)
| Ribonucleoside |
|
|---|---|
| Deoxyribonucleoside |
|
(Nucleoside monophosphate)
| Ribonucleotide | |
|---|---|
| Deoxyribonucleotide | |
| Cyclic nucleotide |
 | This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










